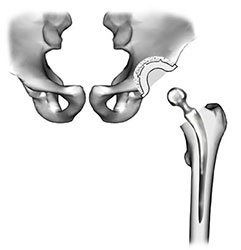
Total Hip Replacement
The aim is to reconstruct the hip joint such that the centre of rotation of the prosthesis is in the same position as that of the hip before the disease started.
Pre-operative Preparation
Include general preparation, antibiotic cover & thromboembolic prophylaxis. Assessment of the acetabulum is crucial as the acetabular component requires at least 90% bone covering. Templating the femoral component is also important as this affects leg length.
Approaches
May be anterolateral, lateral (direct or transtronchanteric) or posterior.
Procedure
- After exposure of the hip joint, resect the femoral head & neck.
- Start preparing the acetabulum by placing anterior acetabular retractors to avoid injury to the femoral artery & nerve or fracture of wall of the acetabulum.
- Ream the bony acetabulum to convert it into a hemisphere & drill fixation holes with a small drill.
- After selection of the acetabular component, the bone is cleaned & dried with hydrogen peroxide soaked swabs.
- Apply the cement under pressure & the acetabular component is then inserted in its correct orientation until the cement is set.
- Carefully identify the medullary canal of the femur by identifying the insertion of piriformis into the greater trochanter.
- Prepare the medullary canal with reamers & broaches. By trial reductions assess length, soft tissue tension & joint stability.
- When the canal is clean & dry, low viscosity cement is introduced under pressure with a cement gun & then the prosthetic stem is inserted & held.
Following polymerisation of the cement, the hip is reduced.
Closure & Drainage
In layers, over suction drains after thorough irrigation.
Postoperative Management
- Continue antibiotics for 24-48 hours.
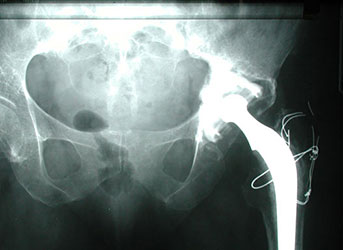
- Check x-rays.
- Start full weight-bearing from the second day.
- Avoid actions that might cause dislocation, such as sitting in low chairs.
- Later on, avoid activities that cause repetitive impact.
Main Postoperative Complications
- Those related to the joint itself - length discrepancy, dislocation, infection, aseptic loosening, femoral fracture & implant failure.
- General complications - Neurovascular injury, urinary tract complications & thromboembolism.